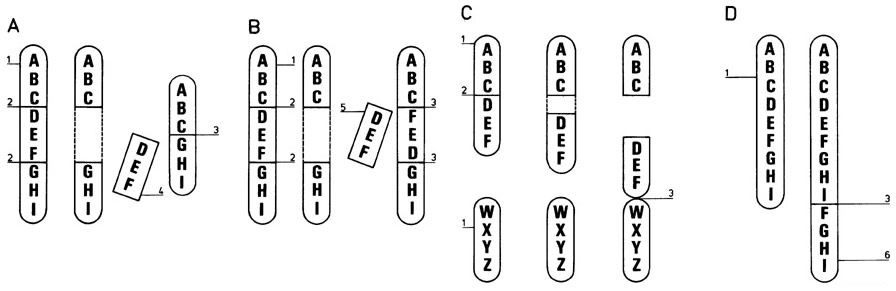
Chromosome Mutations. Inversion (B) Deletion (A) Duplication (D)

Mutation of Chromosomes

Chromosomal mutations. Images from Purves et al., Life: The Science of

All of our chromosomes

including gene mutations, larger chromosomal mutations and genome

Chromosomal aberrations Edit Chromosomal aberrations section

Chromosomes come in pairs with half of each inherited from each parent.

Main article: Chromosome abnormalities

Mutation of Chromosomes - from the Access Excellence site
![[edit] Classification of mutation types [edit] Classification of mutation types](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/26/Chromosomes_mutations-en.svg/301px-Chromosomes_mutations-en.svg.png)
[edit] Classification of mutation types

approach to isolate mutations. This approach uses a balancer chromosome

How do chromosomal mutations take place ? The deficiencies are easiest to

Changes in genes or chromosomes are called mutations .

MUTATION These mutations affect large portions of the chromosomes and are
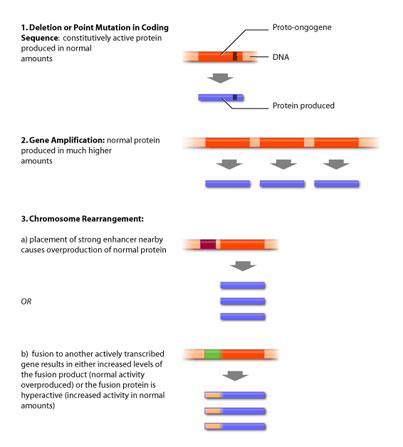
ways: point mutation, gene amplification or chromosomal rearrangements.

Types of structural chromosome changes

macro-mutations or chromosomal mutation or aberration

So radiation can provoke both major types of mutations, point mutations and

colour blindness is typically caused by a mutation on the X-chromosome,

caused by mutations in a person's genes.















No comments:
Post a Comment