
R" wave analagous to the "pathological Q" wave of an anterior MI.

Old inferior wall infarction as evidenced by pathological Q waves in

Significant pathological Q waves (V2-6, I, aVL) plus marked ST segment

There is a pathological Q wave in aVl (width more than 40 msec).
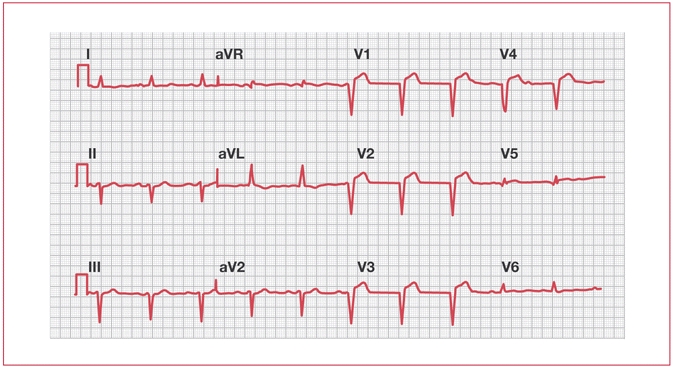
ECG demonstrating abnormal Q waves in V1–V4.

pathological Q-waves in leads V1-V3 (presumably from an old infarction),

contractions and premature atrial contractions, pathological Q-waves in
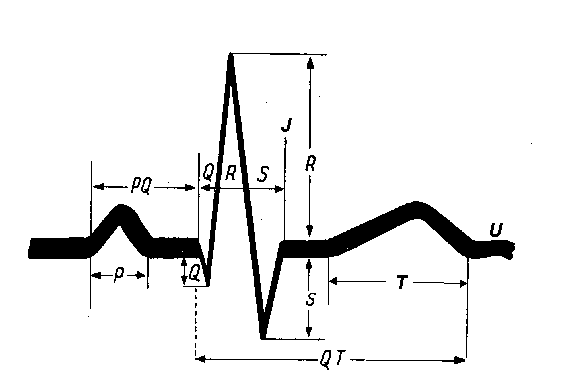
Wave Q: maximum 0.5 mV QRS complex – maximum 0.06 s

However, a pathological Q wave is defined as :

Q waves are often interpreted as evidence of myocardial necrosis but they

Pathological Q waves in inferior and anterior leads

Post myocardial infarction ECG wave tracings

Myocardial Infarction is a Stronger Determinant of Pathological Q Waves
New Q waves: From the absence of depolarization current in the dead tissue

The appearance of pathological Q waves is the most characteristic ECG

and twenty-five (39%) presented a pathological Q wave on the EKG.

A pathological Q wave is a box wide. The inferior leads include leads II,

A pathological Q wave is a box wide. The septal leads are V1 - V2.
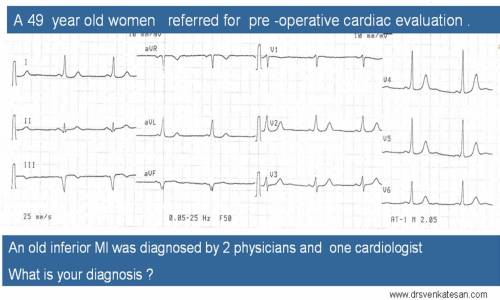
Beware of non infarct q waves : A women with an unusual pathological q waves
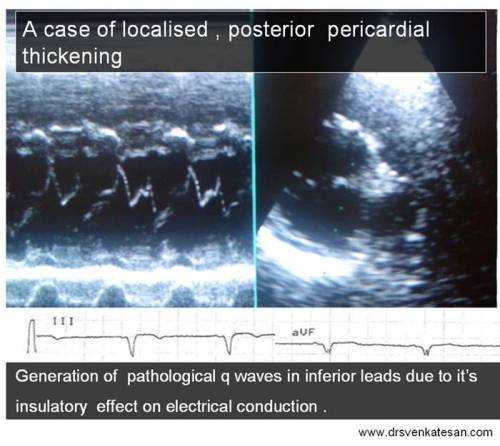
An unusual cause for pathological q waves















No comments:
Post a Comment